Examples¶
Prebuilt VirtualBox¶
A good starting point to build an APK are prebuilt VirtualBox images, where the Android NDK, the Android SDK, and the Kivy Python-For-Android sources are prebuilt in an VirtualBox image. Please search the Download Section for such an image. You will also need to create a device filter for the Android USB device using the VirtualBox OS settings.
Hello world¶
If you don’t know how to start with Python for Android, here is a simple tutorial for creating an UI using Kivy, and make an APK with this project.
Note
Don’t forget that Python for Android is not Kivy only, and you might want to use other toolkit libraries. When other toolkits will be available, this documentation will be enhanced.
Let’s create a simple Hello world application, with one Label and one Button.
Ensure you’ve correctly installed and configured the project as said in the Prerequisites
Create a directory named
helloworld:mkdir helloworld cd helloworld
Create a file named
main.py, with this content:import kivy kivy.require('1.0.9') from kivy.lang import Builder from kivy.uix.gridlayout import GridLayout from kivy.properties import NumericProperty from kivy.app import App Builder.load_string(''' <HelloWorldScreen>: cols: 1 Label: text: 'Welcome to the Hello world' Button: text: 'Click me! %d' % root.counter on_release: root.my_callback() ''') class HelloWorldScreen(GridLayout): counter = NumericProperty(0) def my_callback(self): print 'The button has been pushed' self.counter += 1 class HelloWorldApp(App): def build(self): return HelloWorldScreen() if __name__ == '__main__': HelloWorldApp().run()
Go to the
python-for-androiddirectoryCreate a distribution with kivy:
./distribute.sh -m kivy
Go to the newly created
defaultdistribution:cd dist/default
Plug your android device, and ensure you can install development application
Build your hello world application in debug mode:
./build.py --package org.hello.world --name "Hello world" \ --version 1.0 --dir /PATH/TO/helloworld debug installd
Take your device, and start the application!
If something goes wrong, open the logcat by doing:
adb logcat
The final debug APK will be located in bin/hello-world-1.0-debug.apk.
If you want to release your application instead of just making a debug APK, you must:
Generate a non-signed APK:
./build.py --package org.hello.world --name "Hello world" \ --version 1.0 --dir /PATH/TO/helloworld release
Continue by reading http://developer.android.com/guide/publishing/app-signing.html
See also
- Kivy demos
- You can use them for creating APK too.
Compass¶
The following example is an extract from the Compass app as provided in the Kivy examples/android/compass folder:
# ... imports
Hardware = autoclass('org.renpy.android.Hardware')
class CompassApp(App):
needle_angle = NumericProperty(0)
def build(self):
self._anim = None
Hardware.magneticFieldSensorEnable(True)
Clock.schedule_interval(self.update_compass, 1 / 10.)
def update_compass(self, *args):
# read the magnetic sensor from the Hardware class
(x, y, z) = Hardware.magneticFieldSensorReading()
# calculate the angle
needle_angle = Vector(x , y).angle((0, 1)) + 90.
# animate the needle
if self._anim:
self._anim.stop(self)
self._anim = Animation(needle_angle=needle_angle, d=.2, t='out_quad')
self._anim.start(self)
def on_pause(self):
# when you are going on pause, don't forget to stop the sensor
Hardware.magneticFieldSensorEnable(False)
return True
def on_resume(self):
# reactivate the sensor when you are back to the app
Hardware.magneticFieldSensorEnable(True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
CompassApp().run()
If you compile this app, you will get an APK which outputs the following screen:
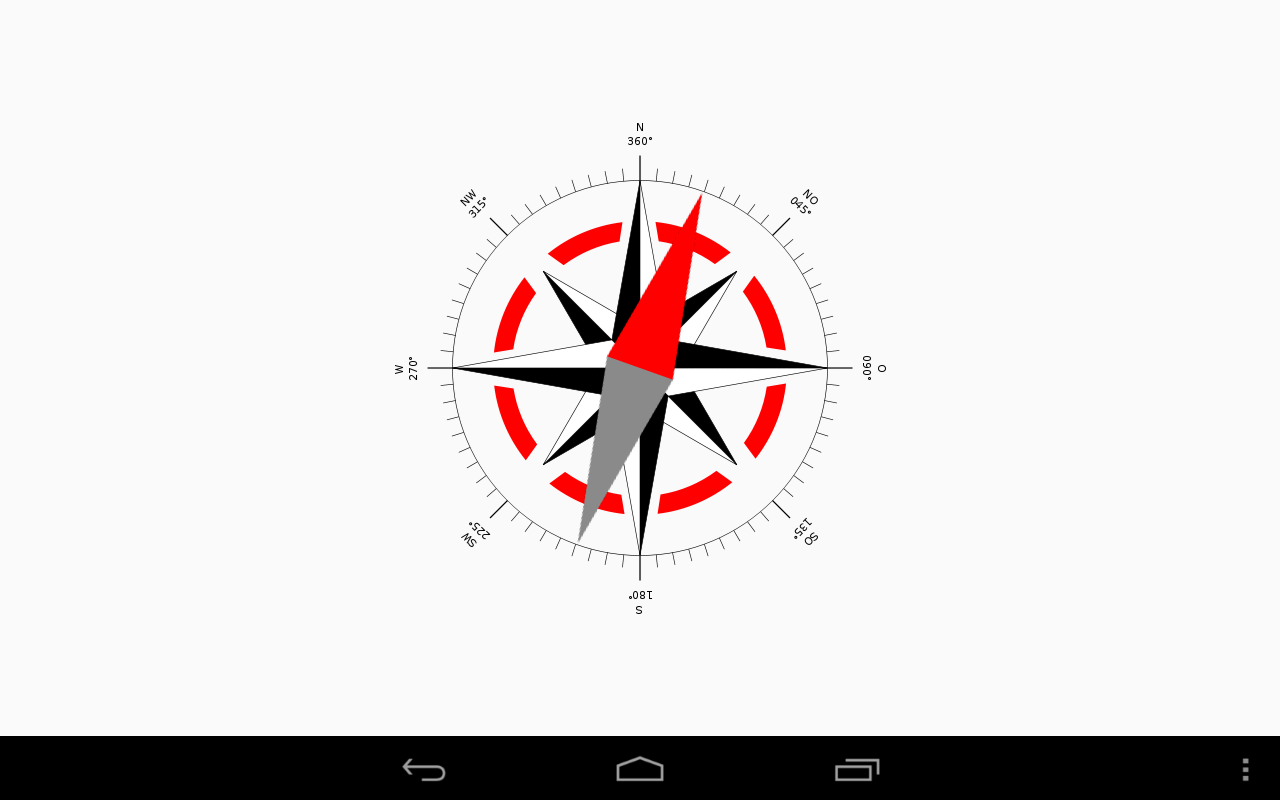
Screenshot of the Kivy Compass App (Source of the Compass Windrose: Wikipedia)